Automating ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes with job scheduling tools can save time, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. ETL workflows move and prepare data from multiple sources for analysis, and when paired with automation, they eliminate manual intervention. Here's the key takeaway: job scheduling tools like Apache Airflow and Databricks Lakeflow streamline ETL by automating task execution, timing, and monitoring.
Why Automate ETL?
- Manual ETL processes are error-prone and time-consuming.
- Automation reduces processing time by 30–50% and operational costs.
- Scales easily with growing data volumes.
How Job Scheduling Works:
- Define Tasks: Set up jobs with specific inputs, outputs, and dependencies.
- Schedule: Use time-based schedules (e.g., daily at 2:00 AM) or event-based triggers (e.g., file arrivals).
- Monitor: Get alerts and retries for failed tasks to ensure smooth execution.
Tools to Consider:
- Apache Airflow: Python-based, supports complex workflows with rich monitoring features.
- Databricks Lakeflow Jobs: Ideal for Spark-based workloads, integrates with Databricks' ecosystem.
Steps to Automate ETL:
- Pick a Tool: Choose based on your infrastructure and team expertise.
- Set Up Jobs: Define tasks, dependencies, and configure schedules.
- Use Triggers: Automate workflows with time-based or event-driven triggers.
By automating ETL, businesses can focus on analysis rather than maintenance, unlocking insights faster and cutting costs. With tools like Airflow and Databricks, the process becomes reliable and scalable.
How to build and automate a python ETL pipeline with airflow on AWS EC2 | Data Engineering Project
Tools and Prerequisites for ETL Job Scheduling
Automating ETL workloads requires the right mix of tools and technical know-how. Fortunately, there are plenty of open-source options available, making automation accessible even for smaller businesses working with limited budgets.
Job Scheduling Tools for ETL
Apache Airflow is a widely-used orchestration platform that allows workflows to be represented as Python-based DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs). It uses operators like PythonOperator and BashOperator to define tasks. Airflow version 3.1.6 supports Python versions 3.10 through 3.13. Its versatility makes it a great choice for managing tasks across multiple platforms, such as CRMs, accounting software tools, and data warehouses. Notably, version 2.2 introduced "Datasets" scheduling, which allows workflows to trigger automatically when specific data objects are updated upstream.
Databricks Lakeflow Jobs is another strong contender, particularly for Spark-based workloads. It supports a variety of task types, including notebooks, Python scripts, and SQL queries, and integrates seamlessly with Unity Catalog for data governance. If your data infrastructure already relies on the Databricks ecosystem, this tool is a natural fit.
Both tools offer time-based scheduling using Cron expressions (e.g., 0 0 * * * for daily midnight runs) and event-driven triggers that respond to changes like file arrivals or table updates.
Technical Requirements
To handle ETL job scheduling effectively, you'll need a solid grasp of Python for creating workflows in Airflow, as well as Bash scripting for command-line tasks. A working knowledge of SQL is also helpful, especially for optimizing queries to save memory and boost performance.
Managing your Python environment is crucial to avoid version conflicts - tools like pip can help here. Additionally, you'll need a metadata database. While SQLite is fine for local testing, PostgreSQL or MySQL are better suited for production environments to track job states and history reliably. For local development, Docker Compose can simplify launching essential services, and setting the AIRFLOW_HOME variable helps manage configurations and logs.
Other key skills include understanding task dependencies, managing job concurrency, and implementing retry logic. Designing idempotent ETL jobs is also critical to prevent duplicates or unintended changes. For event-driven triggers, avoid conditions that are always true (like checking if a file exists), as these can cause jobs to trigger endlessly.
With the right tools and expertise in place, you're ready to start automating your ETL workflows step by step.
Step-by-Step Guide to Automating ETL Workloads
Step 1: Choose a Job Scheduling Tool
Start by selecting a scheduling tool that aligns with your technical setup, team expertise, and growth requirements. Integration flexibility is key - tools like Apache Airflow provide robust connections to AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, Snowflake, and dbt using "Providers" and "Hooks". If you're already using Databricks, Databricks Lakeflow Jobs might be the better choice.
Databricks Lakeflow Jobs offers scalability but comes with task and concurrency limits, so keep those in mind.
Consider your team's preferred workflow. If they lean toward coding, tools like Airflow or Dagster (both Python-based) provide flexibility. For teams that value simplicity, visual interfaces like those in Databricks Lakeflow can streamline configuration. Monitoring features are equally important - look for tools with dashboards, task-level logs, and notification systems that integrate with email, Slack, or webhooks.
To minimize operational overhead, explore managed services like Amazon MWAA, Google Cloud Composer, or Astronomer Astro for Airflow.
| Feature | Apache Airflow | Databricks Lakeflow Jobs | Dagster |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Interface | Python Code (DAGs) | Visual UI & REST API | Python Code (Assets) |
| Scheduling Types | Cron, Timetables, Event-driven | Time-based, File arrival, Table update, Continuous | Cron, Partitions, Sensors |
| Scalability | High (Distributed via Celery/Kubernetes) | Up to 1,000 tasks per job | High (Asset-based orchestration) |
| Monitoring | Rich Web UI, Task Logs, Gantt Charts | System tables, UI dashboards, Notifications | Integrated UI for assets and jobs |
| Best For | Complex, multi-platform orchestration | Databricks-native Spark/ETL workloads | Data-asset centric pipelines |
Once you've chosen your tool, you're ready to start configuring your ETL jobs.
Step 2: Set Up and Configure ETL Jobs
After selecting your tool, the next step is to configure ETL jobs by defining tasks and their dependencies. In Apache Airflow, these tasks are organized within Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), which map out the workflow of your ETL pipeline. Begin by creating a default_args dictionary to set parameters like retries, delays, and dependency logic - these settings are inherited by all tasks in your workflow.
Define your DAG with a unique identifier, start date, and schedule interval. Tasks within the DAG can use operators like BashOperator for shell commands, PythonOperator for custom scripts, or KubernetesPodOperator for containerized tasks. Use operators such as t1 >> t2 or set_downstream to establish task sequences.
To make your workflow dynamic, leverage Jinja templating. For example, templates like {{ ds }} allow tasks to process specific data intervals automatically, eliminating the need for manual updates. Before deploying, test your setup with commands like airflow tasks test to ensure everything runs smoothly and templates render correctly.
Avoid using datetime.now() in your logic, as it can disrupt backfilling for historical data. For workflows spanning multiple time zones, rely on timezone-aware objects from the Pendulum library to avoid scheduling errors.
Once tasks are configured and validated, you can shift focus to automating their execution with scheduling and triggers.
Step 3: Configure Scheduling and Triggers
To automate ETL workflows, set up schedules and triggers. For time-based schedules, use Cron expressions or presets like @daily (midnight runs), @hourly, or @weekly. For continuous workflows, use @continuous to start a new run immediately after the previous one ends.
Event-driven triggers are another option, activating workflows based on external signals like file arrivals in S3, table updates, or message queue notifications. With Airflow 3.0, BaseEventTrigger distinguishes event-compatible triggers from standard ones, ensuring efficient event handling. To avoid infinite loops, configure triggers to respond only to specific events rather than continuously polling.
For data-driven workflows, tools like Airflow (3.0+) and Dagster offer asset-aware scheduling, where jobs are triggered by updates to specific data assets. Use classes like AssetWatcher to monitor external data sources or message queues for real-time reactions.
Always define an execution_timezone (e.g., America/Los_Angeles) for time-sensitive workflows to avoid issues during Daylight Savings Time transitions. Most schedulers default to UTC unless specified otherwise. To prevent resource overload, configure "max concurrency" limits. If the system reaches capacity, new runs are typically skipped.
| Trigger Type | Behavior | Example Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduled | Runs based on a time-based cron expression or interval | Airflow, Databricks, Dagster |
| File Arrival | Triggers when new files land in monitored storage | Databricks Lakeflow |
| Table Update | Triggers when a specific source table is updated | Databricks Lakeflow |
| Asset-Aware | Triggers when a specific data asset is updated upstream | Airflow (Datasets), Dagster |
| Continuous | Starts a new run immediately after the previous one ends | Airflow (@continuous), Databricks |
sbb-itb-d1a6c90
Best Practices for Reliable ETL Automation
Managing Dependencies and Handling Errors
Effectively managing task dependencies is key to avoiding delays and unnecessary resource usage. Design workflows so that smaller, lightweight tasks run on cost-effective instances, while more resource-intensive tasks are assigned to high-performance instances. For example, always ensure that upstream tasks are completed on time to avoid holding up dependent jobs.
From the outset, incorporate robust error-handling mechanisms. Studies highlight that the frequency of incidents and delays in resolving them are common pain points in ETL workflows. As Tim Mitchell, a seasoned data architect, aptly put it:
"On a long enough timeline, every single ETL process will eventually fail." – Tim Mitchell, Data Architect
To minimize disruptions, make ETL jobs idempotent by using "overwrite" methods and direct failures to Dead Letter Queues (DLQs) to isolate problematic data. Set limits for automatic reruns and configure notifications - via tools like Slack or email - to promptly inform stakeholders of any issues.
| Error Handling Type | Action | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Synchronous | Stops the entire pipeline immediately | Critical data like financial or compliance information requiring strict consistency |
| Asynchronous | Isolates bad records while processing valid data | High-volume or real-time streaming scenarios |
With dependencies managed and error-handling safeguards in place, the next step is to focus on improving performance.
Optimizing Performance
After addressing dependencies and errors, shift your focus to making ETL jobs run more efficiently. Avoid placing heavy computations or database queries directly in the top-level job code, as this can cause significant slowdowns. Instead, move resource-intensive library imports (like pandas or TensorFlow) inside task-specific functions to optimize execution.
Whenever possible, offload large-scale computations to your data platform instead of handling them within the scheduler. Use macros or platform-native scripts (e.g., on Snowflake or BigQuery) to process data in smaller, manageable partitions - such as by date - to maintain idempotency and enable efficient incremental updates.
Sensors can help ensure that jobs only start once all upstream dependencies are ready, reducing the risk of failures caused by delayed data. Limit the number of concurrent job runs to prevent bottlenecks, and for larger ETL projects, consider running documentation generation as a separate task to avoid memory overflows during primary transformations.
Advancements in orchestration tools, like the release of Prefect 3.0 in 2024, have significantly reduced runtime overhead - by as much as 90%. Additionally, multi-threading capabilities allow schedulers to handle multiple paths in a DAG simultaneously, with default thread counts often set at four. These improvements can drastically enhance the efficiency of your ETL processes.
Conclusion
ETL Automation Benefits: Cost Savings and ROI Statistics
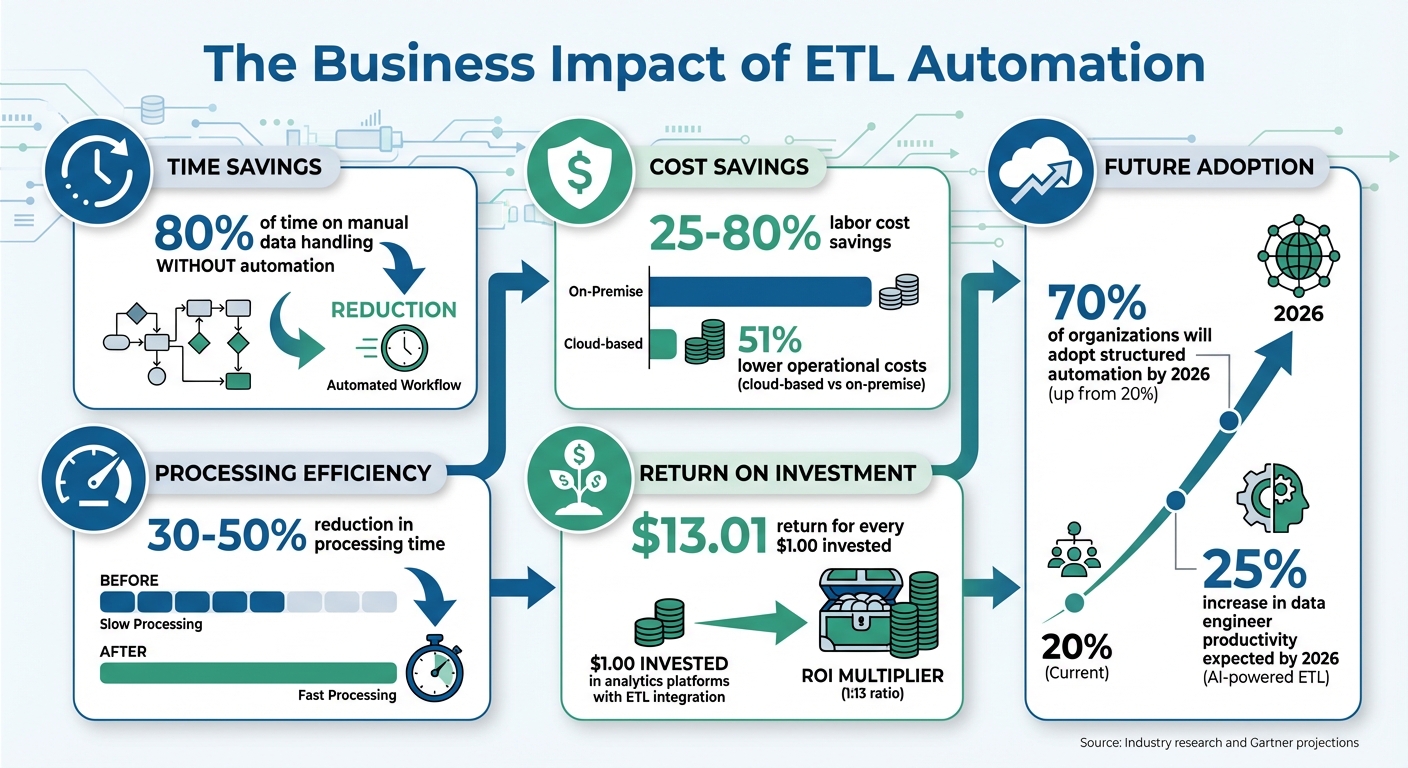
Automating ETL workloads with job scheduling tools is changing the way businesses manage their data. By cutting down on manual tasks, reducing errors, and freeing up time, teams can shift their focus from tedious data processing to more strategic efforts. Instead of dedicating 80% of their time to manual data handling, automation takes care of the repetitive work, allowing your team to concentrate on analysis and growth.
The financial advantages are impressive too. Companies using ETL automation report labor cost savings ranging from 25% to 80%, while cloud-based solutions lower operational costs by 51% compared to on-premise systems. Even more striking, for every $1.00 invested in analytics platforms powered by ETL integration, businesses can achieve returns as high as $13.01.
For small businesses, the benefits are clear. Job scheduling tools offer enterprise-grade data reliability without the need for complex infrastructure or a larger IT team. As Brandon Gubitosa, Head of Content & Communications at Rivery, explains:
"ETL automation offers significant benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced data accuracy and quality, reduced human error, and overall cost savings".
The push toward automation is only gaining momentum. According to Gartner, 70% of organizations will adopt structured automation by 2026, a sharp rise from just 20% in the past. AI-powered ETL tools are also expected to increase data engineer productivity by an additional 25% by 2026. Now is the time to embrace automated job scheduling. With reliable data pipelines, your business can access timely insights to grow your business fast with efficient tools that fuel innovation.
FAQs
What are the main advantages of using job scheduling to automate ETL processes?
Automating ETL processes with job scheduling brings a range of advantages that can transform how data workflows are managed. For starters, it boosts efficiency by cutting down on manual tasks and speeding up processes. This not only minimizes the risk of human error but also ensures consistent and accurate data updates across your systems.
Another major perk? It saves both time and money. By automating repetitive tasks, your team can shift their focus to more strategic, high-value activities, all while keeping your data pipelines running seamlessly and on schedule.
What’s the difference between Apache Airflow and Databricks Lakeflow for automating ETL workflows?
Apache Airflow takes a workflow-first approach, where you define ETL tasks as Python-based Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). These DAGs outline the task sequence, dependencies, and schedules. Airflow uses an external scheduler and a metadata database to handle execution. While it's great for orchestrating intricate workflows, it demands more manual setup and infrastructure management.
Databricks Lakeflow, in contrast, adopts a data-first approach with built-in governance and event-driven triggers. You can create workflows using a visual interface or API, and they can be triggered automatically by events like new files, table updates, or scheduled times. This eliminates the need to manage separate schedulers or metadata stores, offering a more integrated and simplified way to handle data pipelines.
To put it simply, Airflow is geared toward custom workflow orchestration, while Lakeflow prioritizes data-driven automation with less infrastructure complexity.
What skills are needed to successfully automate ETL workflows with job scheduling?
To effectively automate ETL workflows, you'll need a combination of technical know-how and hands-on experience. Here are some key skills to focus on:
- Grasping ETL fundamentals: Understanding how to design and map datasets between sources and targets is essential for building workflows that can be reused and scaled.
- Programming expertise: Proficiency in a language like Python is often a must since it's widely used for crafting job definitions and scheduling tasks.
- Mastering cron expressions: Knowing how to write accurate cron expressions ensures your workflows run at the right times without hiccups.
- Managing time zones: Configuring jobs to align with local time zones, such as America/Los_Angeles, helps avoid timing conflicts and keeps processes consistent.
- Working with cloud platforms: Familiarity with tools like Databricks or Google Cloud Scheduler is invaluable for setting up triggers and managing complex schedules.
- Debugging and monitoring: Being able to troubleshoot errors, analyze logs, and configure alerts is crucial for ensuring workflows run smoothly and reliably.
Developing these skills will enable you to design, schedule, and maintain ETL workflows that align with your specific business requirements, especially in a U.S. setting.


