Managing database changes in CI/CD pipelines is challenging due to the stateful nature of databases. Mistakes in schema updates can lead to downtime, data loss, or performance issues. To address these risks, automated tools streamline version control, drift detection, and rollbacks, ensuring consistency across environments. This article highlights five tools that simplify database change management:
- Liquibase: Offers ChangeLogs and ChangeSets for version control, rollback options, and support for over 60 databases.
- Flyway: Uses SQL migration scripts, supports Git-based workflows, and integrates with popular CI/CD tools.
- Redgate SQL Change Automation: Focuses on SQL Server and Oracle, with pre-deployment checks and detailed change reports.
- DBmaestro: Combines state-based and migration-based approaches, with rollback strategies and compliance tracking.
- Bytebase: Provides GitOps workflows, schema drift detection, and 1-click rollbacks for safe deployments.
Each tool has unique features tailored to specific use cases, from simple SQL migrations to enterprise-grade compliance. Below is a quick comparison to help you decide.
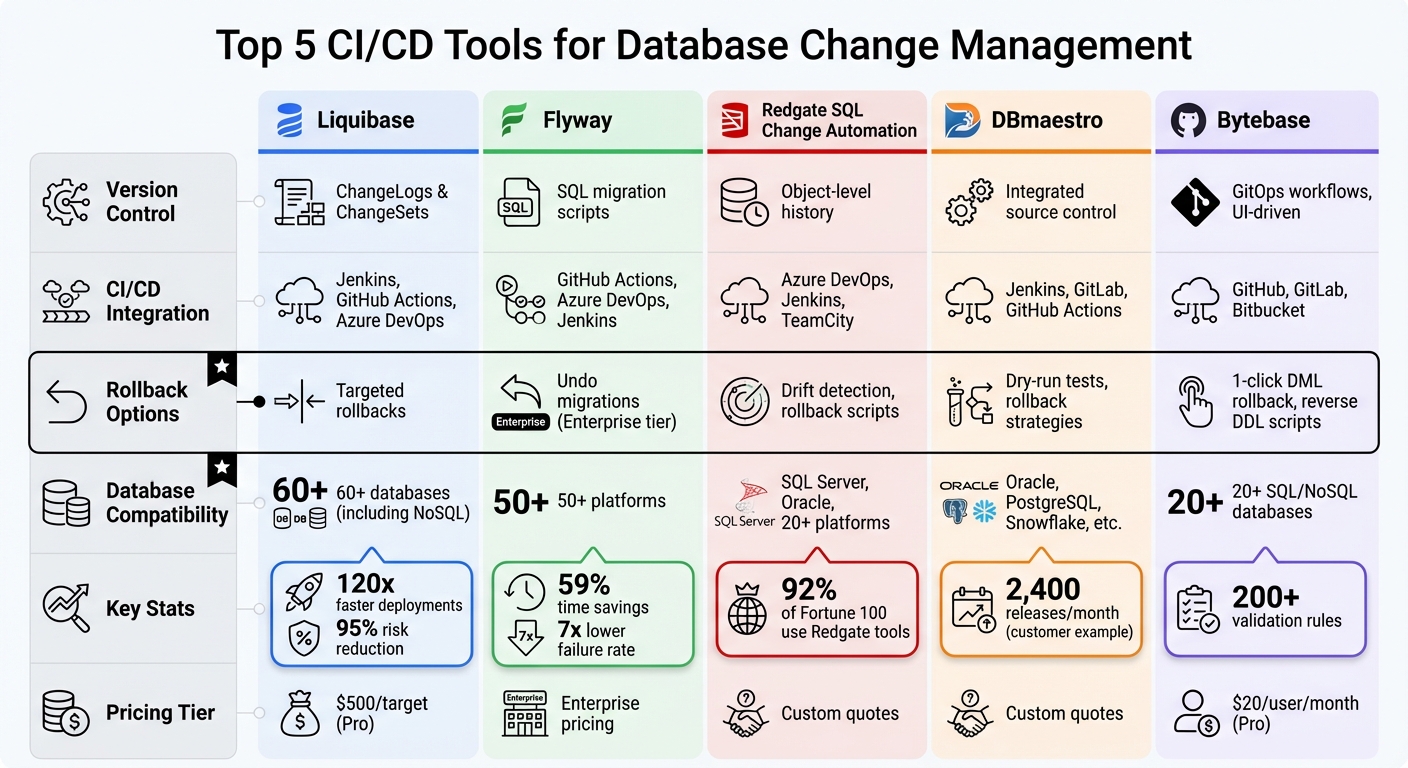
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Version Control | CI/CD Integration | Rollback Options | Database Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquibase | ChangeLogs, ChangeSets | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps | Targeted rollbacks | 60+ databases, including NoSQL |
| Flyway | SQL migration scripts | GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, Jenkins | Undo migrations (Enterprise tier) | 50+ platforms |
| Redgate SQL Change Automation | Object-level history | Azure DevOps, Jenkins, TeamCity | Drift detection, rollback scripts | SQL Server, Oracle, 20+ platforms |
| DBmaestro | Integrated source control | Jenkins, GitLab, GitHub Actions | Dry-run tests, rollback strategies | Oracle, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, etc. |
| Bytebase | GitOps workflows, UI-driven | GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket | 1-click DML rollback, reverse DDL scripts | 20+ SQL/NoSQL databases |
These tools reduce deployment risks, improve efficiency, and ensure database consistency, making them essential for integrating databases into modern CI/CD workflows.
CI/CD Database Tools Comparison: Features, Integration & Compatibility
CI/CD for database - 2 devops tools for DB versioning and migration | liquibase and flyway

1. Liquibase
Liquibase simplifies managing database schema changes by organizing them into individual ChangeSets, which are stored in ChangeLogs. These ChangeSets can be written in SQL or in more flexible, database-independent formats like XML, JSON, or YAML, making it easier to handle multi-platform deployments. Plus, Liquibase integrates smoothly with version control systems to keep track of these changes.
Version Control for Schema Changes
ChangeLogs can be stored in Git, ensuring version control for database changes. Liquibase also uses a DATABASECHANGELOG table to track which changes have been applied, preventing duplicate or conflicting updates and safeguarding data integrity.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Liquibase works seamlessly with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Maven, Spring Boot, and Docker. By running Java 8 or later on your CI/CD pipeline, you can automate database updates using actions like setup-liquibase, eliminating the need for manual reviews. Santhosh Kumar Gunasekaran, DevOps Lead at Synchrony Financials, shared:
Liquibase helped to efficiently manage database changes, reduced deployment friction and allowed App teams to focus more on innovation.
Rollback Capabilities
Liquibase offers precise rollback options, letting you revert to a specific ChangeSet, deployment ID, date, or tag without affecting other updates. This flexibility reduces the risks associated with errors. As Robert Harrison, Technical Director at i360, explained:
The cost of failure is greatly reduced because we know sooner and can more easily address it. With Liquibase Secure, we know exactly where every change came from and when it was made, which is a huge advantage.
Database Compatibility
Liquibase supports over 60 database platforms, including popular SQL databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server, as well as NoSQL databases, data lakes, and cloud data warehouses such as BigQuery and Redshift. With Liquibase Secure, you can achieve deployments up to 120 times faster while reducing deployment risks by 95%.
2. Flyway
Flyway uses a "schema-as-code" approach to manage database changes, letting teams track updates through plain SQL scripts or schema models. These scripts can be stored in popular Git-based platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, as well as in Subversion and TFS. The tool offers two deployment methods: migrations-based, which uses incremental scripts for precise control, and state-based, which compares the current database to a target schema model. Flyway keeps a record of every change in a flyway_schema_history table, logging details such as which migrations were applied, who applied them, and when. This setup makes Flyway an easy fit for modern CI/CD workflows.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Flyway simplifies database deployments with its CLI, Java API, Maven, and Gradle tools, and it integrates seamlessly with CI/CD platforms like Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, and Octopus Deploy. You can also use Docker to pull the latest version, eliminating the need for manual installations on build agents. Dave Syer, Senior Consulting Engineer at Pivotal, shared his thoughts:
Database migrations are something that Java developers struggle with, and Redgate Flyway offers a tool simple enough for anyone with basic SQL knowledge.
Companies using Flyway report impressive results: a 59% reduction in deployment time, a 7x lower rate of change failures, and efficiency gains valued at approximately $1.88 million. Notably, Redgate solutions are trusted by 92% of the Fortune 100.
Rollback Capabilities
Flyway includes rollback functionality with its "Undo" migrations feature. Its "Fail Fast" mechanism ensures that the process stops immediately if an issue or inconsistent state is detected. For more complex setups, the Enterprise edition offers advanced features like compliance checks and drift detection to ensure rollback safety.
Database Compatibility
Flyway supports an extensive range of over 50 databases, including SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Snowflake, Google BigQuery, and even preview support for MongoDB. It has earned a TrustRadius rating of 8.5/10 based on 13 reviews. With continuous development since 2010, Flyway remains a reliable choice for database change management.
3. Redgate SQL Change Automation
Redgate SQL Change Automation simplifies database change management by adopting a state-based approach. It organizes each database object into separate SQL files, neatly arranged in folders. These files seamlessly integrate with popular version control systems like Git, Azure DevOps (TFS), Subversion, and Mercurial. Developers can commit changes directly from familiar tools like SSMS or Visual Studio. The tool tracks every change - who made it, when, and why - while also managing dependencies to ensure changes are deployed in the correct order.
Version Control for Schema Changes
To help teams work efficiently, the tool includes object locking within SSMS, preventing team members from accidentally overwriting each other's work. It also offers advanced filtering to exclude certain objects, such as users and permissions, from tracking.
Now integrated into Redgate Flyway Enterprise, the tool supports both state- and migration-based approaches. Migration scripts are particularly useful for handling more complex changes, like renaming tables or splitting columns. These features create a solid foundation for integrating with CI/CD pipelines.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Building on its robust version control capabilities, Redgate SQL Change Automation streamlines CI/CD workflows. The process typically involves two main stages:
- Build Stage: Validates the project and creates a deployment package.
- Release Stage: Deploys the package, runs tests, and generates key artifacts.
Redgate offers native add-ons for tools like Azure DevOps, TFS, Octopus Deploy, TeamCity, Bamboo, and Jenkins. GitLab users can integrate via PowerShell cmdlets or Docker containers. During the pipeline process, the tool runs tSQLt tests and validates migration scripts against a temporary database, helping catch errors early. Before deploying to production, it generates detailed release artifacts, including change reports, drift reports, and the exact SQL script to be executed. With over 200,000 customers worldwide, including 92% of the Fortune 100, Redgate tools are trusted by some of the largest organizations.
Rollback Capabilities
In addition to its deployment features, Redgate SQL Change Automation reduces risk with rollback capabilities. Using the SQL Compare engine, it generates rollback scripts to undo changes if needed. Drift detection is also built into the release process, ensuring the target database schema hasn’t changed since the release was prepared. Many companies using Redgate Flyway report faster deployment times, with releases completed in minutes and significant time saved through automation. Grant Fritchey, Product Advocate at Redgate, highlighted the value of this feature:
You also instantly receive a unique ability that's normally not achievable with a database, the ability to undo certain changes... if you make a change there, but then want to change it back, source control gives you the exact code you had before.
Database Compatibility
While SQL Change Automation focuses primarily on SQL Server, its state-based deployment features also extend to Oracle, PostgreSQL, and MySQL through Flyway Enterprise. As part of the larger Flyway Enterprise ecosystem, it connects to over 50 database platforms. Additionally, Redgate’s customer support receives high praise, with 87% of users rating it as "Excellent".
sbb-itb-d1a6c90
4. DBmaestro

DBmaestro stands out in the database change management landscape with its hybrid approach. By combining state-based migrations with immutable deployment scripts, it ensures consistent and repeatable processes while accommodating differences across environments. The platform leverages Git for tracking scripts and migration logic, creating a single source of truth for all database changes.
Version Control for Schema Changes
DBmaestro excels at tracking schema drift, supports branching with conflict detection, and maintains detailed audit trails for every change. Tim McKean, a Data Architect at Elevance Health, shared his experience:
DBmaestro allowed us to control changes made to the database and promote those changes in an easy and controlled way.
The platform also performs dry-runs and impact analyses before deployment, catching potential errors early in the process.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
DBmaestro integrates seamlessly with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitLab, and GitHub Actions, enabling automated database changes to align with application code pipelines. This integration has driven significant improvements for its users. For example, a US Fortune 250 company reduced release times from six days to just 15 minutes. Another organization, a major HR software provider, increased its release frequency from a single release to an astonishing 2,400 releases per month. Similarly, one enterprise transitioned from manual releases every three weeks to 2,300 automated releases monthly.
The platform also tracks DORA metrics - deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and time to restore service - providing teams with valuable insights into their performance.
Rollback Capabilities
Failures during deployment are handled smoothly with DBmaestro’s automated rollback features. These mechanisms revert schema changes, configurations, and data updates as needed. The platform even tests downgrade plans during the CI process, ensuring rollback strategies are ready before being required in production. For instance, an international bank adopted DBmaestro’s self-service database delivery approach, achieving 60 releases per day. By using the same workflows for rollbacks and deployments, consistency is maintained throughout the process.
Database Compatibility
DBmaestro supports a wide array of databases, including Oracle, MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, IBM DB2, Snowflake, Redshift, MongoDB, Amazon RDS/Aurora, and Databricks. It also offers connectivity to any database via JDBC. Additionally, it integrates with security tools like CyberArk Vault, AWS Secret Manager, and Azure Key Vault.
Pricing for DBmaestro is available through custom quotes, with three enterprise plans - Dev, Sec, and Ops. The platform has earned a solid 8.0/10 rating on TrustRadius based on five reviews. With its broad database support and advanced features, DBmaestro proves to be a versatile solution for managing diverse database environments.
5. Bytebase

Bytebase provides two distinct workflows to manage database changes: a UI-driven console for centralized control and a GitOps workflow that keeps migration scripts alongside application code. This dual approach allows teams to rely on the GitOps method for routine deployments while switching to the UI-driven console for urgent hotfixes or sensitive production updates.
Version Control for Schema Changes
Bytebase uses Git repositories (like GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Azure DevOps) as the single source of truth for migration scripts. It actively monitors databases to detect schema drift - unauthorized changes made outside the CI/CD pipeline - and immediately notifies teams. Each schema change is validated against over 200 rules to ensure proper syntax, performance, and security standards. For large-scale operations, Database Groups streamline batch changes across multiple databases, whether you're managing 10 or 10,000. This makes it particularly well-suited for multi-tenant SaaS architectures.
These features lay a solid foundation for integrating with CI/CD pipelines.
CI/CD Pipeline Integration
Building on its version control capabilities, Bytebase integrates effortlessly into modern CI/CD workflows. By linking your Git repository, you can trigger automated migrations via API, complete with environment-specific rollout paths (e.g., Dev → Test → Staging → Prod). The platform supports structured multi-environment pipelines, offering tailored environment policies and risk-based approvals. For instance, development changes might be auto-approved, while production updates require multi-level reviews.
Rollback Capabilities
Bytebase also ensures safe rollbacks for database changes. With its 1-Click Rollback feature, the platform captures snapshots of affected rows before executing Data Manipulation Language (DML) operations like UPDATE or DELETE. These snapshots are stored in a dedicated bbdataarchive database, making it easy to restore the original state. For schema changes, Bytebase generates reverse migration scripts to revert the database structure to its prior state. It even supports rolling back multiple related changes across different databases in one operation. However, rollbacks are subject to certain limits: SQL statements must be under 2MB, cannot mix DDL and DML, and require a primary key for UPDATE operations.
Database Compatibility
Bytebase supports a wide range of databases - over 20 SQL and NoSQL types, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, TiDB, Oracle, SQL Server, and Amazon Aurora. This broad compatibility makes it a versatile option for diverse infrastructure setups. Additionally, Bytebase integrates with tools like Terraform, allowing teams to manage environments, databases, and SQL review rules programmatically for greater efficiency.
Tool Comparison Table
Here's a quick look at how the five tools stack up in terms of their main features:
| Tool | Version Control | CI/CD Integration | Rollback Options | Database Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquibase | ChangeLog system with ChangeSets | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, GitLab, CircleCI, Bamboo | Targeted rollback functions | 60+ databases, including NoSQL, data lakes, and warehouses |
| Flyway | Schema-as-code using SQL migration scripts | GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, GitLab, Jenkins, Octopus Deploy | Undo migrations (Enterprise tier) and callback scripts | 50+ database platforms |
| Redgate SQL Change Automation | Object-level history with automated migration script generation | GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, Jenkins, TeamCity | Drift detection with pre-deployment checks and change reports | 20+ platforms, optimized for SQL Server and Oracle |
| DBmaestro | Integrated source control with pipeline-ready automation | Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, GitLab, CircleCI | Dry-run tests with rollback strategies | Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, MySQL |
| Bytebase | Dual workflow: UI-driven and GitOps-based | GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps | One-click DML rollback and reverse DDL migration scripts | 20+ SQL and NoSQL types, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MongoDB |
This table highlights the specific strengths and compatibility of each tool, helping you decide which one aligns best with your CI/CD needs.
Liquibase leads the pack with support for over 60 databases, making it a versatile choice for diverse projects. Flyway, with compatibility across 50+ platforms, is another flexible option. Redgate SQL Change Automation, on the other hand, is tailored for SQL Server and Oracle environments, offering robust pre-deployment checks to ensure smooth rollouts. DBmaestro focuses on enterprise-level security and compliance, supporting major databases like Oracle and PostgreSQL. Bytebase stands out for its dual workflow approach, combining a user-friendly interface with GitOps-based automation, along with features like one-click rollbacks and multi-environment rollouts.
When it comes to pricing, Liquibase Pro starts at $500 per target, while Bytebase Pro costs $20 per user/month. The other tools, including Redgate SQL Change Automation and DBmaestro, typically require custom enterprise quotes. For teams just starting out with database CI/CD, Liquibase, Flyway, and Bytebase also offer free community or open-source editions, making them accessible options for smaller projects or testing phases. In contrast, Redgate and DBmaestro are positioned as enterprise-level solutions, ideal for organizations with complex needs and larger budgets.
Conclusion
Effectively managing database changes within CI/CD pipelines is achievable with the right tools. The five options discussed - Liquibase, Flyway, Redgate SQL Change Automation, DBmaestro, and Bytebase - tackle common challenges like drift detection, automated rollbacks, and policy enforcement, all of which are critical to minimizing deployment failures and production downtime.
Each tool shines in different scenarios, making it easier to align solutions with your team's specific needs. For smaller to mid-sized teams working across various database platforms, Liquibase and Flyway are excellent choices, especially since both offer free community editions for trial use. Developer-focused teams that treat database schema as code will appreciate how GitOps-friendly tools like Flyway and Liquibase integrate seamlessly with platforms such as GitHub Actions, GitLab, and Azure DevOps. On the other hand, enterprises with strict compliance requirements (e.g., SOX, HIPAA, GDPR) may find Liquibase Secure and DBmaestro especially useful for their tamper-evident audit logs and automated policy checks.
For multi-tenant SaaS companies managing numerous regional databases, Bytebase's Database Groups feature stands out, enabling controlled rollouts across thousands of instances. The impact of these tools is evident: Flyway users report saving 59% of time per deployment and experiencing a sevenfold reduction in change failure rates. Similarly, Liquibase users have seen deployment speeds improve by 120x, with a 95% reduction in risk.
If you're starting out, focus on automating less critical database objects first. This approach helps build confidence before moving on to core production schemas. Drift detection should also be prioritized early on, as manual hotfixes are a frequent cause of deployment failures. Whether you prefer a UI-driven workflow (offered by Bytebase or DBmaestro) or a GitOps-based approach (with Flyway or Liquibase), integrating database changes into your CI/CD pipeline is key to smoother, more reliable deployments.
FAQs
How do CI/CD tools manage database rollbacks?
CI/CD tools handle database rollbacks by offering features such as version control, targeted rollbacks, and automated processes. These functionalities enable teams to undo specific changes or migrations, ensuring smooth deployments while protecting data integrity.
For instance, some tools rely on versioned or undo scripts to safely reverse changes, while others manage dependencies to ensure schema alterations can be rolled back without complications. This approach simplifies the rollback process, minimizes risks, and keeps database changes well-organized within CI/CD pipelines.
What’s the difference between state-based and migration-based approaches in managing database changes?
When it comes to managing database changes, state-based and migration-based approaches take distinct paths.
State-based methods focus on comparing the existing database schema with a target model. From there, they automatically generate the necessary changes to bring the two into alignment. While this method is efficient and quick, it doesn't offer much flexibility for fine-tuning individual updates.
On the other hand, migration-based methods handle changes incrementally through scripts. These scripts let you manage updates step by step, offering more control over the process. You can track, adjust, and even reorder specific changes, making this approach particularly useful in complex systems or team-based projects.
How do these tools support compliance with regulations like GDPR or SOX?
These tools simplify the process of meeting regulations like GDPR and SOX by embedding security, governance, and audit controls directly into database change workflows. They take care of automating and documenting every change, making sure modifications are fully traceable, auditable, and in line with regulatory standards.
With features like role-based access, version tracking, and automated reporting, these tools give organizations complete oversight and control over database updates, helping to minimize the risk of falling out of compliance.