Why are diversity dashboards important? They transform workforce data into visual charts, making it easier to track representation, identify equity gaps, and monitor progress in real time. Unlike static reports, these dashboards help organizations act quickly by identifying early indicators like hiring trends or pay disparities.
What makes customization essential? Every organization has unique challenges. Custom dashboards allow companies to tailor metrics, visuals, and reports to their specific needs, whether it's tracking hiring diversity in a small startup or monitoring pay equity in a large corporation.
Key metrics to track:
- Representation: Workforce demographics by race, gender, age, etc.
- Talent Flow: Hiring, promotions, retention rates.
- Pay Equity: Median pay comparisons and promotion opportunities.
- Inclusion: Employee sentiment, psychological safety, and belonging.
How to build one:
- Set clear goals: Define what data to track and who will use it.
- Centralize data: Combine HR, payroll, and survey data into one system.
- Visualize effectively: Use simple, clear visuals like bar charts and heat maps.
- Ensure privacy: Anonymize data and apply safeguards for small groups.
Common challenges and solutions:
- Privacy risks: Use anonymization techniques like data suppression.
- Accuracy issues: Assign data stewards, automate updates, and audit regularly.
- Bias in metrics: Break down data by demographics to uncover disparities.
Integration tips: Link dashboards to HR systems for real-time updates. Automated connections ensure data stays current, reducing manual errors. This allows organizations to track trends like engagement scores or promotion rates instantly.
Why it matters: Companies with diverse leadership see up to 36% higher profitability. Dashboards not only improve transparency but also help organizations act decisively to close equity gaps and retain talent. Start small, focus on key metrics, and expand as your DEI initiatives grow.
Key Metrics for Diversity Dashboards
Core DEI Metrics
Start by establishing a baseline with representation data. This includes tracking workforce composition across categories like race, ethnicity, gender, age, sexual orientation, disability status, and veteran status.
Next, focus on talent flow - hiring, promotions, and retention. This helps uncover demographic-specific challenges. For instance, only 54 Black women are promoted to entry-level manager roles for every 100 men, creating a gap that widens at higher leadership levels. Monitoring these patterns can highlight barriers early on.
Pay equity is another critical area. Compare median pay, starting salaries, and promotion opportunities. Research shows that gender-diverse leadership teams are associated with 25% higher profitability, while ethnically diverse teams see a 36% boost. While these core metrics show who is present and advancing in the organization, deeper insights come from examining the quality of inclusion.
Advanced Metrics for Inclusion
Inclusion metrics go beyond the basics to assess whether everyone in the organization feels valued and heard. The Gartner Inclusion Index, for example, evaluates inclusion through seven dimensions: fair treatment, integrating differences, decision-making, psychological safety, trust, belonging, and diversity. Companies that measure DEI effectively and integrate inclusion into talent decisions report up to 20% higher organizational inclusion.
"Inclusion remains the most difficult metric to track... organizations must measure employee sentiment with a considered definition of inclusion." - Gartner
Behavioral indicators also play a role. These include the use of inclusive language in job postings, identifying high-potential talent across demographics, ensuring workspace accessibility, and encouraging participation in employee resource groups. It's also important to examine intersectional experiences, such as those of middle-aged female immigrants who are also mothers, to understand the complexities of layered identities.
Instead of relying solely on annual surveys, consider using pulse surveys to capture shifts in employee sentiment more frequently, especially in hybrid work settings. Breaking down your Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) by demographic can help pinpoint satisfaction gaps. For example, nearly half of Hispanic employees (49%) and Black employees (47%) have left jobs after witnessing or experiencing discrimination.
sbb-itb-d1a6c90
Diversity & Inclusion KPI Dashboard in Power BI
How to Build a Custom Diversity Dashboard
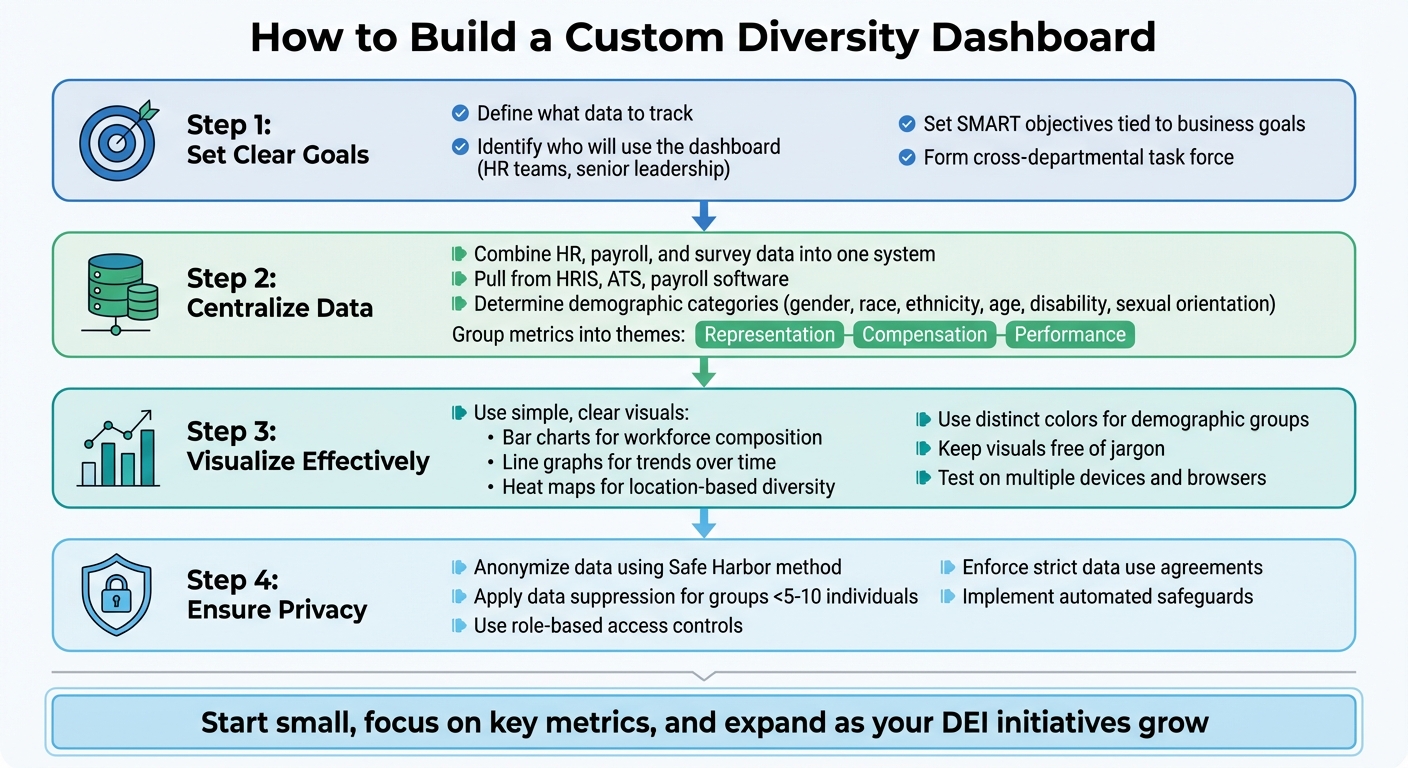
4-Step Guide to Building Custom Diversity Dashboards
Define Objectives and Data Requirements
Start by identifying who will use the dashboard. For example, HR teams might need detailed data for hiring and succession planning, while senior leadership may prefer high-level overviews. As Peter Hoopis, CEO of Peter Hoopis Ventures, shared:
"We built our DEI dashboard with HR in mind because they were the major user of the data. We wanted to be sure that we hire equitably".
Form a cross-departmental task force to ensure the dashboard aligns with your organization’s values. Set clear, SMART objectives that tie directly to your business goals, such as addressing representation gaps, pay equity, or promotion trends.
Next, determine where your data will come from. Most organizations pull information from systems like Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS), Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), payroll software, and employee engagement surveys. Decide which demographic categories - such as gender, race, ethnicity, age, disability status, and sexual orientation - you’ll analyze, and group metrics into themes like representation, compensation, and performance.
Use inclusive, human-centered language throughout the process. For instance, replace technical terms like "non-resident aliens" with "international employees" after consulting with diverse employee groups about their preferences. Keep in mind that as your DEI goals evolve, your objectives and data requirements should adapt as well.
Data Collection and Standardization
Bring together data from HRIS, ATS, payroll, and equity platforms into one centralized system to maintain consistency. Gauri Manglik, CEO of Instrumentl, highlighted the benefits of this approach:
"Before we created a diversity dashboard, we used an annual survey... Now we can look at our DEI dashboard every week and see if there are any trends over time".
Switching from annual surveys to more frequent data updates allows you to spot trends in real time and respond more effectively.
Standardize demographic labels by consulting employee groups to ensure language is inclusive. Normalize data across various dimensions - like departments, management levels, office locations, and hire dates - to uncover meaningful patterns. For example, when evaluating compensation, include base salary, bonuses, and equity to get a full picture of wealth distribution.
Also, calibrate performance metrics across demographic groups to identify potential biases. The Atlantic, as cited by ChartHop, noted:
"African American employees tend to receive more scrutiny from their bosses than their white colleagues, meaning that small mistakes are more likely to be caught, which over time leads to worse performance reviews and lower wages".
Analyzing performance ratings by race, ethnicity, and gender can expose systemic disparities.
Benchmark your internal data against industry standards or national statistics to provide context. Combine quantitative data with qualitative insights from exit surveys and focus groups to better understand trends like high turnover. Finally, prioritize data security and anonymization to protect sensitive information and build employee trust.
Once your data is unified and standardized, the next step is to focus on making it visually compelling and easy to understand.
Design and Visualization Best Practices
Choose visualizations that clearly communicate your data. For example, line graphs can show trends in pay equity or engagement scores over time, stacked bar charts can display workforce composition by race or gender, and heat maps can highlight diversity across office locations. As ChartHop pointed out:
"Visualizing this data is powerful - images stick in your mind more than numbers, and certainly more than cells in a spreadsheet".
Use distinct colors to represent different demographic groups and keep visuals simple and free of jargon so they’re accessible to everyone, from executives to entry-level employees. Test the dashboard on multiple devices (like mobile and desktop) and browsers (Chrome, Safari, Firefox) to ensure it works seamlessly.
Connecting the dashboard directly to your HRIS or ATS platforms enables real-time updates, reducing manual errors and keeping the data current. Start small by tracking a few key metrics, and expand as your DEI initiatives mature. Comparing internal KPIs with industry benchmarks or past performance can also provide valuable insights.
Take inspiration from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s 2011 redesign of healthy eating guidelines. By shifting from a "food pyramid" to a "plate model", they made the information more relatable. Applying this principle to your DEI dashboard can help users better understand and engage with the data by presenting it in formats that resonate with them.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Creating effective diversity dashboards comes with its share of challenges, particularly around privacy, accuracy, and bias. Addressing these issues is key to delivering meaningful and reliable insights.
Data Privacy and Anonymization
Safeguarding employee information is a critical concern. Even when direct identifiers like names are removed, individuals can still be identified. For example, research highlights that combining details like birth date, gender, and a 5-digit ZIP code can uniquely identify more than 50% of U.S. residents. This risk becomes even more pronounced in smaller teams or leadership levels, where demographic profiles are more distinct.
Legal teams often worry that collecting diversity data could create a "paper trail" that might be used in discrimination lawsuits. As Bias Interrupters explains:
"In-house lawyers often worry that collecting diversity data may yield evidence of discrimination that can fuel lawsuits against them. But there are ways to minimize the legal threats while still embracing the use of metrics."
To address these concerns, organizations can adopt practices like the "Safe Harbor" method, which involves removing 18 specific identifiers to protect anonymity. Other strategies include using data suppression (e.g., grouping ages into 5-year ranges or only reporting metrics when groups include at least 5–10 individuals) and seeking expert determination to ensure minimal re-identification risk . When sharing dashboard access with managers or external parties, enforce strict data use agreements to prevent attempts at re-identifying employees.
Once privacy is secured, the next step is ensuring your data remains accurate and up-to-date.
Maintaining Data Accuracy
While privacy measures are essential, accurate data forms the backbone of any reliable dashboard. In fact, data inaccuracies cost organizations an average of $12.9 million annually. For diversity dashboards, accuracy depends on five key factors: completeness (all necessary fields are filled), accuracy (data reflects reality), consistency (data is uniform across systems), timeliness (information is current), and traceability (data lineage is clear).
To achieve this, assign data stewards - dedicated individuals responsible for verifying and updating records. Implement Master Data Management (MDM) systems to centralize employee data, eliminating inconsistencies across departments. Integrate your dashboard with HRIS and ATS platforms to minimize manual entry errors, and use automated tools to flag anomalies before they impact reports .
Regular audits are also crucial. These should include testing system controls, reviewing workflows, and sampling datasets to confirm accuracy. Finally, set a consistent refresh schedule - monthly, quarterly, or annually - based on your organization's size and hiring activity.
Bias in Metrics and Analysis
Even the best dashboards can unintentionally perpetuate bias if not carefully designed. A common example is performance ratings, which can be influenced by unconscious bias. As The Atlantic notes:
"African American employees tend to receive more scrutiny from their bosses than their white colleagues, meaning that minor errors are over-scrutinized, which over time leads to worse performance reviews and lower wages."
To uncover and address such disparities, break down performance and compensation data by race, ethnicity, gender, job level, and location . Use tools like the four-fifths rule to detect adverse impact - if the selection rate for a protected group is less than 80% of the highest-scoring group, there may be inequity. When analyzing pay, investigate whether lower averages stem from pay inequities or underrepresentation in higher-paying roles.
Finally, collect diversity data through voluntary self-reporting rather than relying on managers' observations. This approach not only ensures accuracy but also respects employees' identities.
Integrating Dashboards with Business Tools
After addressing privacy and accuracy concerns, the next logical step is linking your diversity dashboard to the tools your organization already relies on. Integration not only eliminates tedious manual data entry but also ensures your metrics stay current, reflecting real-time organizational changes instead of outdated snapshots.
Connecting with HR and Recruitment Platforms
Your diversity dashboard becomes far more effective when it pulls data directly from your ATS (Applicant Tracking System) and HRIS (Human Resource Information System). By using REST APIs and automated data feeds, you can consolidate payroll, performance reviews, and engagement survey data into one centralized view.
Take TechCorp Global as an example. In Q4 2024, they used the Sopact Sense platform to integrate sponsorship programs with clear promotion criteria. By tracking these initiatives through a real-time dashboard, they achieved a 27% increase in the representation of women and underrepresented minorities in director-level roles and above. They also improved their diverse talent retention rate from 74% to 91%.
A critical part of successful integration is assigning unique, persistent identifiers to every employee across all systems. This step prevents data fragmentation, which often forces analysts to waste up to 80% of their time reconciling duplicate records. Gauri Manglik, CEO of Instrumentl, highlights the benefits:
"Now we can look at our DEI dashboard every week and see if there are any trends over time - are people more satisfied with their work now than they were before? ... This helps us identify where we need to focus our efforts for improvement".
These integration techniques provide the foundation for continuous, real-time tracking.
Real-Time Reporting and Updates
Switching from quarterly PDF reports to live dashboards represents a major shift in how diversity metrics are tracked. Traditional reporting methods, which often take 4–6 weeks to deliver insights, only offer a look at past conditions rather than current realities.
Modern dashboards, powered by automated data feeds and API connections, update metrics in real time as changes occur in your systems. Whether it's a new hire completing onboarding, a promotion, or feedback from a pulse survey, this information flows instantly into your dashboard. With this real-time data, you can monitor leading indicators like 90-day engagement scores and interview-to-offer ratios, helping you predict future retention and hiring trends.
For instance, platforms like ADP provide API templates specifically designed for employee demographics and payroll data. These templates use OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 authentication to securely automate data sharing between systems. This automation minimizes manual entry errors and ensures your dashboard reflects the latest workforce changes. As Unmesh Sheth, Founder & CEO of Sopact, puts it:
"The gap isn't commitment - it's visibility. Without real-time measurement, DEI becomes reactive rather than strategic".
To protect privacy while maintaining functionality, implement role-based access controls and automated data suppression for groups with fewer than five individuals. This allows managers to filter and analyze data independently without compromising confidentiality.
Conclusion
Benefits of Custom Diversity Dashboards
Custom diversity dashboards empower organizations to make data-driven decisions by offering real-time insights into equity and inclusion metrics. With these tools, leadership teams can spot challenges - such as a decline in retention rates among specific demographic groups - and take immediate action, rather than waiting for quarterly reports to reveal the issue.
The impact of inclusive workplaces is undeniable. Companies with gender-diverse leadership teams are 25% more likely to achieve high profits, and inclusive cultures are six times more likely to drive innovation while generating over twice the cash flow per employee. Dashboards also promote transparency and accountability by clearly displaying workforce composition, pay disparities, and promotion rates, which is vital when nearly half of Hispanic (49%) and Black (47%) employees report leaving jobs due to discrimination.
In addition to fostering equity, these dashboards help organizations identify high-potential talent from underrepresented groups and provide the necessary support for their advancement.
Getting Started with Implementation
Custom dashboards simplify DEI tracking, but a thoughtful implementation strategy ensures their effectiveness. Begin by defining your audience - whether it's HR, leadership, or external stakeholders - and tailor the dashboard to meet their needs. Assemble a cross-department task force to incorporate diverse viewpoints into the design process.
Prioritize three key metric areas: representation (workforce demographics), compensation (pay equity), and performance (promotion rates and engagement). Integrating the dashboard with existing business administration tools like HRIS or ATS platforms helps automate updates and minimize manual errors. To safeguard privacy, use role-based access controls and aggregate data for smaller groups.
Start small by focusing on a few critical metrics, then expand based on user feedback. Offer training resources, such as videos or guides, to help managers interpret the data effectively. For instance, in August 2023, Simon Bacher, CEO of Ling App, utilized Google Data Studio to create color-coded graphs tracking recruitment goals. This visual approach allowed his leadership team to quickly identify trends and adjust their hiring strategies.
FAQs
What are the benefits of custom diversity dashboards for small organizations?
Custom diversity dashboards give small organizations a clear, visual way to understand their workforce demographics and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) metrics. These tools make it easier to spot underrepresented groups, track progress over time, and evaluate how well inclusion efforts are working. By analyzing data on factors like gender, race, and age, organizations can identify trends and focus on areas that need attention.
What makes these dashboards especially useful is their ability to simplify complex data into actionable insights. Leadership and HR teams can use this information to set measurable goals and clearly communicate progress. Metrics like turnover rates, pay equity, and employee engagement can be tracked in real-time, giving organizations the ability to make informed decisions and adapt strategies as needed. In short, custom diversity dashboards play a key role in building inclusivity, ensuring accountability, and driving meaningful progress in a growing organization.
How can organizations ensure their diversity dashboard data is accurate?
To keep diversity dashboards accurate and reliable, organizations should prioritize a few essential practices. Start by pinpointing and gathering key DEI metrics, such as workforce representation, pay equity, and performance data. Make sure this information is both thorough and relevant to your goals. A critical step here is data validation - always cross-check your sources and confirm the accuracy of the data before adding it to your dashboards.
It's also important to regularly review and analyze trends over time. This helps uncover any inconsistencies or gaps in the data. Align your data collection efforts with specific DEI objectives to ensure the metrics you're tracking are actionable and tied to your broader strategy. By following these steps, you'll not only boost data accuracy but also strengthen the impact of your diversity efforts.
How can diversity dashboards help boost a company's profitability?
Diversity dashboards play a powerful role in improving profitability by offering organizations a clear, data-driven perspective on their diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives. These tools track essential metrics like workforce demographics - such as gender, ethnicity, and age - making it easier to pinpoint areas that need attention and measure the effectiveness of diversity strategies. A more inclusive workplace often leads to benefits like stronger innovation, smarter decision-making, and higher employee engagement, all of which help drive better financial outcomes.
Studies consistently reveal that companies with diverse teams tend to outperform their competitors, showing higher levels of profitability and productivity. Diversity dashboards also encourage accountability by providing real-time tracking of DEI progress and its influence on critical factors like retention, turnover, and collaboration. With these insights, businesses can address biases, cultivate inclusivity, and improve team dynamics, ultimately paving the way for long-term growth and success.


