Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) do more than streamline warehouse tasks - they're essential for protecting sensitive data and meeting strict regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Non-compliance with these rules can lead to severe fines, such as up to €20 million under GDPR or $1.5 million annually for repeated HIPAA violations. WMS platforms safeguard data through encryption, access controls, and audit trails, ensuring secure handling of personal and health information. Here's how WMS supports compliance:
- Encryption: Protects data during storage and transfer.
- Access Controls: Limits data access based on user roles.
- Audit Trails: Tracks system activity for transparency and accountability.
- Regulatory Support: Automates GDPR and HIPAA requirements like data deletion and breach reporting.
Warehouse Technology Trends: Warehouse Management in the Cloud
sbb-itb-d1a6c90
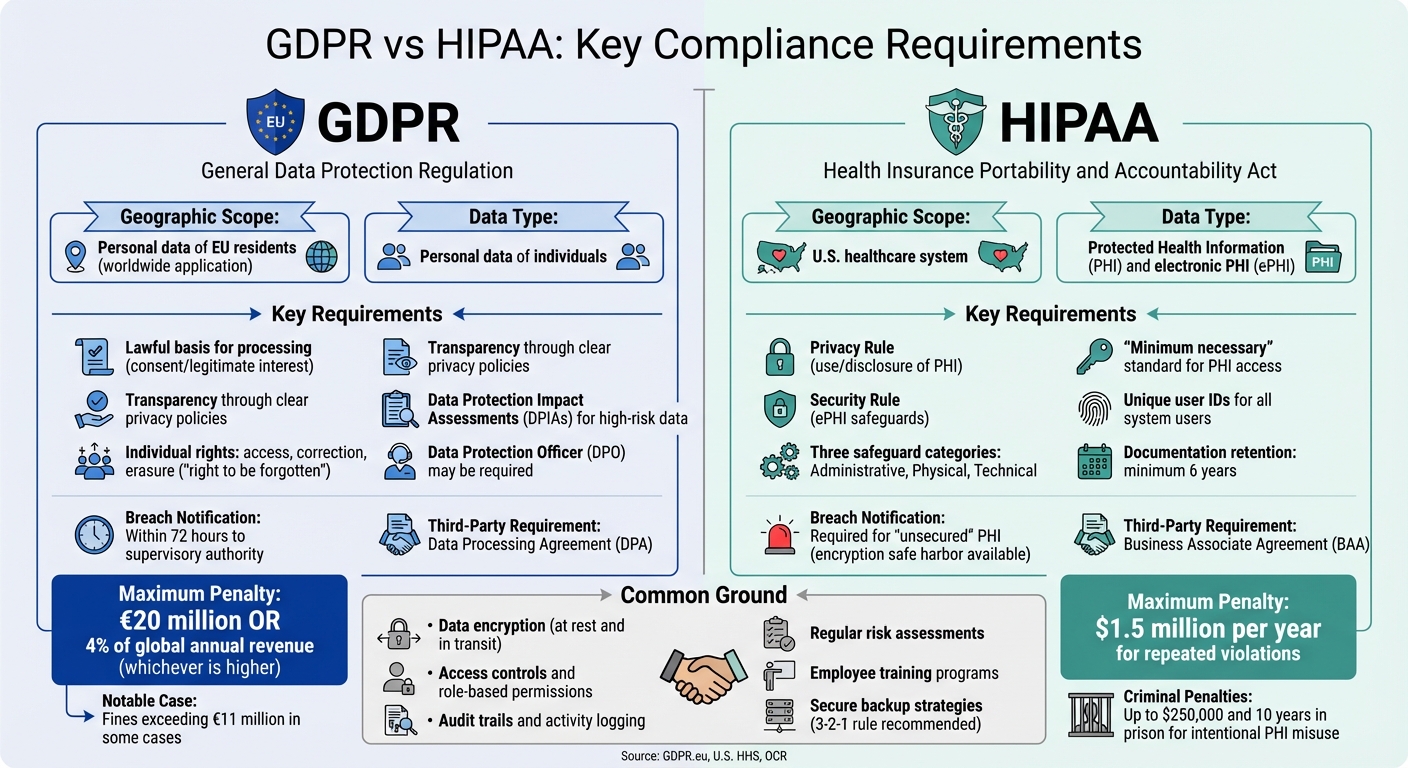
Key Regulations: GDPR and HIPAA
GDPR vs HIPAA Data Compliance Requirements Comparison
Warehouse operators must comply with GDPR and HIPAA to safeguard sensitive data effectively. These regulations set detailed protocols for data handling. GDPR addresses the personal data of individuals in the European Union, while HIPAA focuses on protecting health information within the U.S. healthcare system. Both impose strict penalties for non-compliance and demand strong technical and organizational safeguards.
GDPR: Personal Data Protection
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to any organization processing the personal data of EU residents, regardless of its location. It requires businesses to establish a lawful basis for processing data, such as obtaining explicit consent or using business administration tools to demonstrate a legitimate interest. Transparency is key - clear privacy policies must outline how data is collected and used. GDPR also grants individuals rights over their data, including access, correction, erasure (known as the "right to be forgotten"), and the ability to object to processing. For warehouses, this means their Warehouse Management System (WMS) must support prompt deletion of user records upon request.
GDPR emphasizes integrating data protection into system design from the outset. As GDPR.eu highlights:
[Data protection] needs to be something you and your employees are always aware of.
Organizations handling high-risk data must conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and may need to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO).
Security under GDPR aligns with the CIA triad - confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Article 5(1)(f) of UK GDPR specifies:
Personal data must be "processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the personal data, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage, using appropriate technical or organizational measures."
To meet these standards, warehouses should implement measures like encrypting data both at rest and in transit, enforcing strict access controls on mobile devices such as scanners and tablets, and adopting reliable backup strategies like the 3-2-1 rule (three copies of data on two devices, with one stored off-site). Additionally, in the event of a data breach, organizations have just 72 hours to notify the relevant supervisory authority. Failing to comply with GDPR has led to penalties exceeding €11 million in some cases.
HIPAA: Protected Health Information (PHI) Security
In the U.S., HIPAA establishes strict rules for safeguarding health information. It comprises two key components: the Privacy Rule, which governs the use and disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI), and the Security Rule, which outlines safeguards for protecting electronic PHI (ePHI).
Warehouses handling PHI as part of healthcare operations are classified as Business Associates and are subject to HIPAA penalties. As clarified by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS):
Lacking an encryption key does not exempt a CSP [Cloud Service Provider] from business associate status and obligations under the HIPAA Rules.
HIPAA outlines three categories of safeguards:
- Administrative safeguards: Conduct risk analyses, designate a security official, train employees, and establish contingency plans for data backup and disaster recovery.
- Physical safeguards: Control facility access to systems storing ePHI, secure workstations, and ensure proper disposal of hardware.
- Technical safeguards: Use unique user IDs, implement audit controls to track system activity, and encrypt data transmitted over networks.
HIPAA also enforces a "minimum necessary" standard, meaning PHI use and disclosure must be limited to what is essential for a specific task. Documenting HIPAA policies and assessments is another requirement, with records needing to be kept for at least six years. Warehouses must also sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with any covered entity before handling PHI. For example, the Office for Civil Rights reached a resolution agreement with an organization that stored ePHI for over 3,000 individuals on a cloud server without executing a BAA.
HIPAA offers a safe harbor for breach notifications: if ePHI is encrypted according to HHS standards and the decryption key remains secure, a formal breach report may not be necessary.
| Regulation | Geographic Scope | Breach Notification | Key Third-Party Requirement | Maximum Penalty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Personal data of EU residents | Within 72 hours to authorities | Data Processing Agreement (DPA) | €20 million or 4% of global revenue |
| HIPAA | U.S. Protected Health Information | Required for "unsecured" PHI | Business Associate Agreement (BAA) | $1.5 million per year for repeated violations |
WMS Features That Support Data Compliance
Today's warehouse management systems (WMS) come equipped with tools designed to safeguard sensitive data, control access, and maintain detailed records of system activities. These features integrate security measures into daily operations, helping businesses stay compliant with data regulations while ensuring smooth warehouse functionality.
Data Encryption and Secure Storage
A WMS protects sensitive data by using encryption, which converts information into an unreadable format accessible only to authorized users. As Mintsoft puts it:
"Encryption works like a safe: It turns sensitive information into a mix of letters and numbers that are impossible to read by people who don't have a decryption key." – Mintsoft
Data encryption in WMS covers both storage (data at rest) and transfer (data in transit) through protocols like SSL/TLS and HTTPS, ensuring sensitive information stays secure. Many cloud-based platforms, such as those hosted on AWS, comply with standards like HIPAA/HITECH and GDPR by employing hardware security modules (HSMs) certified to FIPS 140-2 Level 3. These platforms also handle tasks like redundant backups and security updates automatically, reducing manual effort.
For enhanced security, encryption keys should be stored separately from the encrypted data, and advanced systems support automated key rotation. While the HIPAA Security Rule doesn’t mandate specific technologies, the Federal Government’s Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) commonly use 128-, 192-, or 256-bit keys.
Access Controls and Role-Based Permissions
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures employees only access the information needed for their specific roles. For instance, a warehouse picker might only see product locations and quantities, whereas a supervisor could access broader inventory reports and performance metrics. This approach reduces the chances of internal data breaches. HIPAA regulations also require assigning unique identifiers to every system user to ensure accountability when handling electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI).
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security by requiring not just a password but also a secondary verification step, like a code sent to a mobile device. Advanced systems can even detect unusual activities - such as logins from different locations or access attempts during off-hours - and automatically revoke permissions if needed. These measures follow IAM compliance best practices like the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access they require. To further bolster compliance, WMS platforms maintain comprehensive audit trails that track every access and action within the system.
Audit Trails and Reporting Tools
Audit trails in a WMS capture detailed records of user activity, including timestamps, user IDs, and the nature of each action. HIPAA regulations mandate that these logs be retained for at least six years, and they must be protected from unauthorized changes. Modern WMS platforms also provide automated compliance reporting, which continuously monitors system activity. These reports can track, for example, when and by whom a specific customer’s personal data was accessed - offering proof of compliance with regulations like GDPR.
Interestingly, about 89% of organizations now incorporate WMS functionality into their logistics operations, with many achieving inventory accuracy rates above 99%. This reflects how robust compliance features not only meet regulatory demands but also enhance overall operational efficiency.
How to Implement a WMS for Data Compliance
Conducting a Data Audit and Risk Assessment
The first step in ensuring data compliance is conducting a thorough audit to map out sensitive data - where it’s stored, how it moves, and how it’s handled. Use questionnaires across departments to identify vulnerabilities in your current processes.
Next, classify potential threats into three categories: natural (e.g., floods or fires), human (like unauthorized access or accidental deletion), and environmental (such as power outages). The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) underscores the importance of this step:
"Risk analysis is the first step in identifying and implementing safeguards that comply with and carry out the standards and implementation specifications in the Security Rule".
Evaluate each threat based on its likelihood and potential impact.
For organizations under the UK GDPR, it’s crucial to document all non-occasional data processing activities - or all activities if your company has over 250 employees. Risk assessments should also be updated regularly to reflect any technological or operational changes. Similarly, HIPAA requires a comprehensive risk analysis as part of its Security Management Process.
Once risks are clearly defined, you can begin configuring your WMS to align with these regulatory requirements.
Customizing WMS for Regulatory Requirements
Using insights from your risk assessment, configure your WMS to address vulnerabilities and meet compliance standards. For GDPR compliance, this means enabling automated data lifecycle management with strict retention and erasure policies. Your system should also allow for easy retrieval, correction, deletion, and export of customer data in user-friendly formats to support data portability. Implement role-based access controls to ensure employees only access the data they need.
For HIPAA compliance, focus on technical safeguards for electronic Protected Health Information (e-PHI). This includes enforcing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) and adopting a "3-2-1" backup strategy: maintain three copies of data, store them on two different devices, and keep one copy off-site for disaster recovery. HIPAA also mandates that covered entities protect the PHI of deceased individuals for 50 years. As the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services explains:
"HIPAA included Administrative Simplification provisions that required HHS to adopt national standards for electronic health care transactions and code sets, unique health identifiers, and security".
Additionally, ensure all third-party integrations - such as those with shipping carriers or e-commerce platforms - comply with your WMS’s security protocols. Establish data processing agreements where required. Under GDPR, any data breach must be reported to the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of detection.
Employee Training and Documentation
Proper training is critical for ensuring compliance. According to the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO):
"It is therefore vital that your staff understand the importance of protecting personal data, are familiar with your security policy and put its procedures into practice".
Training should cover the roles and responsibilities of data controllers and processors, recognizing phishing attempts, verifying caller identities, and adhering to acceptable use policies for company systems. Managers should receive live demonstrations to help them quickly identify and resolve issues. Beyond onboarding, regular refresher training is essential to keep staff updated on new policies and emerging threats.
Documentation is another cornerstone of compliance. Maintain detailed records of processing activities (ROPA), including processing purposes, data categories, recipients, and retention schedules. Additionally, document your information security policies, backup procedures, encryption protocols, and breach reporting processes. As the ICO highlights:
"Documenting your processing activities is important, not only because it is itself a legal requirement, but also because it can support good data governance and help you demonstrate your compliance with other aspects of the UK GDPR".
Keeping these records in electronic form makes them easy to search and update as your processes evolve. Together, comprehensive training and meticulous documentation help integrate compliance into your organization’s daily operations.
Conclusion
A compliance-focused Warehouse Management System (WMS) turns data protection into a key advantage. By consolidating sensitive data into one secure platform, these systems make auditing more straightforward, speed up regulatory reporting, and lower the risk of costly violations. And the stakes are no joke - violations can be incredibly expensive. For instance, GDPR fines can hit €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue, while HIPAA penalties can climb to $1.5 million annually for repeated violations. In extreme cases, HIPAA breaches involving intentional misuse of Protected Health Information (PHI) can lead to fines as high as $250,000 and up to 10 years in prison. Beyond compliance, these systems provide a solid foundation for improving business operations and information systems.
In addition to avoiding hefty fines, modern WMS platforms enhance operational efficiency. For example, inventory accuracy often exceeds 99.5%, while labor productivity can improve by 15% to 30%. Features like automated audit trails, role-based access controls, and encryption work together to safeguard data while streamlining day-to-day tasks. As the PULPO WMS Team puts it:
"Ensuring its security is not just a matter of regulatory compliance but also of maintaining business integrity and customer trust".
The move to cloud-native platforms in 2026 has further simplified compliance. With automated security updates, AI-powered threat detection, and flexible global data residency options, businesses can stay ahead of changing regulations without being held back by outdated systems. Whether you're managing pharmaceutical stock under HIPAA or handling customer data under GDPR, a properly configured WMS cuts down on human error, boosts security, and keeps your operations ready for audits.
FAQs
How does a Warehouse Management System (WMS) help meet GDPR and HIPAA compliance standards?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) plays a key role in helping businesses meet regulatory requirements like GDPR and HIPAA by focusing on data security and privacy. These systems incorporate features such as data encryption, user authentication, and access controls to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Many WMS platforms also support secure data transfer protocols and maintain detailed audit trails. This ensures transparency in data handling and aligns with regulatory standards. By automating compliance-related processes, WMS solutions minimize the risk of human error while upholding stringent data protection measures.
How does a WMS help businesses protect sensitive data and meet compliance standards?
A warehouse management system (WMS) plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information while helping businesses stay compliant with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, thanks to its built-in security features.
One of its standout features is data encryption, which safeguards information during both transmission and storage, keeping it out of reach from unauthorized access. Another key element is strict user authentication and role-based access controls, ensuring that only the right personnel can access critical data. To top it off, regular data backups act as a safety net, allowing businesses to recover quickly in case of system failures or cyberattacks.
Together, these features not only shield sensitive data but also help businesses adhere to regulatory standards, reinforcing customer trust and ensuring smooth operations.
Why is encryption essential for a Warehouse Management System?
Encryption plays a crucial role in any Warehouse Management System (WMS) by protecting sensitive data like inventory levels, supplier details, and customer records from prying eyes and cyberattacks. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest, a WMS ensures that only those with proper authorization can access the information, keeping it secure and private.
On top of that, encryption helps businesses meet important data protection standards like GDPR and HIPAA, which mandate strong safeguards for personal and sensitive information. It ensures data stays intact and secure while remaining accessible to authorized users when necessary. This not only shields your operations from potential breaches but also reassures customers that their information is handled with care and security in mind.


